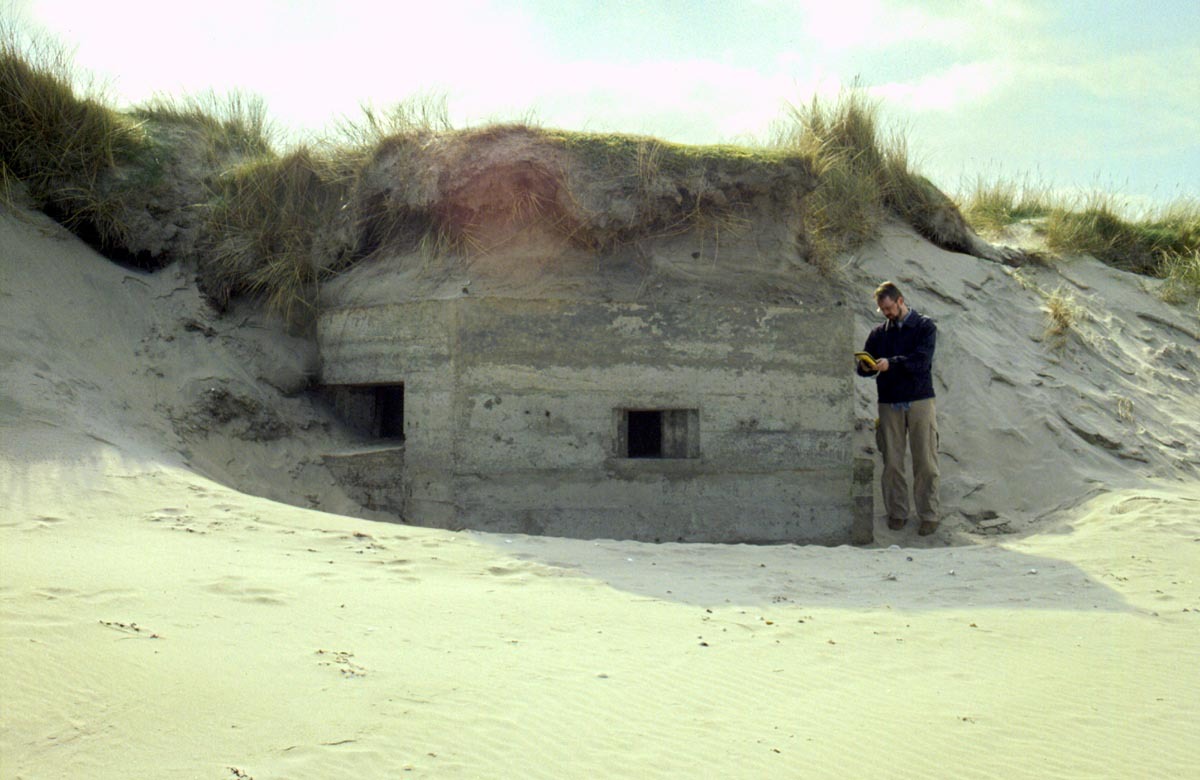
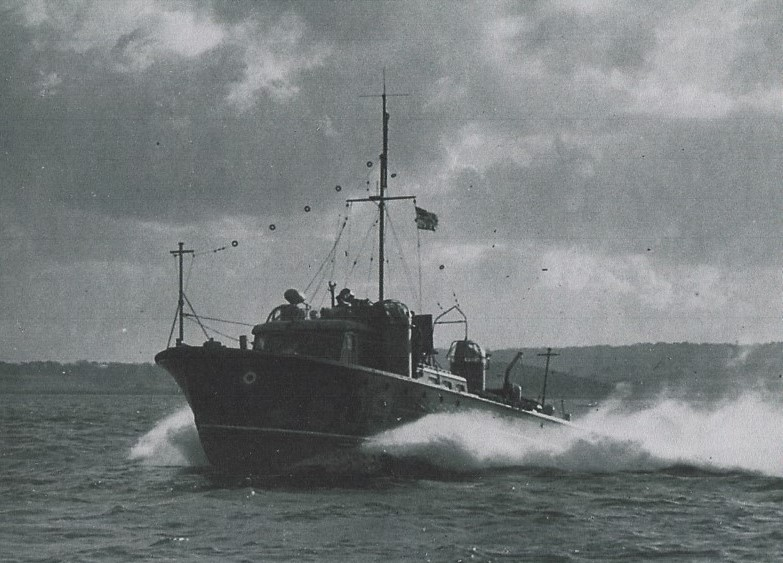
To reduce the likelihood of panic buying and hoarding, the announcement was made on a Sunday while shops were closed, and ration books weren’t issued in advance. While they waited for their clothing ration book to arrive, the public were instructed to use the margarine coupons in the back of their food rationing book when buying clothing and fabric.
Each person initially had 66 clothing coupons to last for twelve months. This was later reduced to 48 coupons the following year. Coupons had to be surrendered for clothing, footwear and cloth. The more fabric and labour needed to produce a piece of clothing, the more points it required. Children’s clothing required fewer points.